-40%
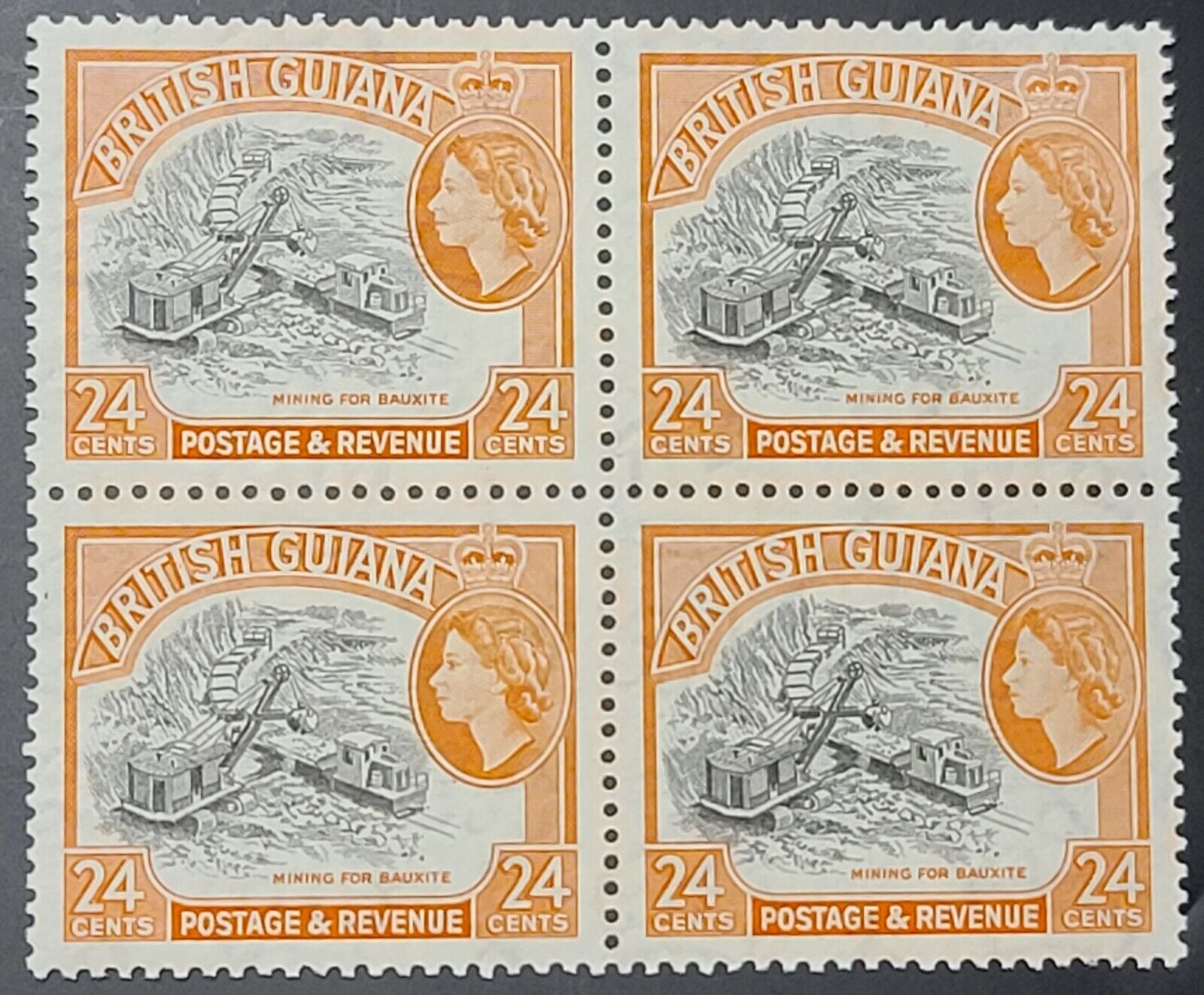
BRITISH GUIANA 1954 Elizabeth II ERA BLOCK STAMPS Sc 261. SG 339 BLOCK OF 4 MNH
$ 17.15
- Description
- Size Guide
Description
Mining for BauxiteBauxite is the material used to make Aluminium pots and pans and all Aluminium products
Large Machinery used to extract Bauxite and shipped on Rails
British Guiana
1954
Watermark 4
Block Stamps of 4
SCARCE
LARGE SELVAGE
MINT NEVER HINGED (MNH)
Era: Elizabeth II (1952 - Now)
Large Stamp Margin
65 Years Old Mint Block Stamps
Same Stamp with Different Stamp Numbering System:
Scott Number: 261 or SC #261
Stanley Gibbons: 339 or SG #339
Michel Number:
Guyana Lot #129
British Guiana
British Guiana
was a British colony, part of the
British West Indies
, which resided on the northern coast of
South America
, now known as the independent nation of
Guyana
since1966.
The first European to encounter Guiana was Sir
Walter Raleigh
, an English explorer. The
Dutch
were the first Europeans to settle there, starting in the early 17th century, when they founded the colonies of
Essequibo
and
Berbice
, adding
Demerara
in the mid-18th century. In 1796, Great Britain took over these three colonies during hostilities with the French, who had occupied the
Netherlands
. Britain returned control to the
Batavian Republic
in1802 but captured the colonies a year later during the
Napoleonic Wars
. The colonies were officially ceded to the United Kingdom in 1814 and consolidated into a single colony in 1831. The colony's capital was at
Georgetown
(known as Stabroek prior to 1812). The economy has become more diversified since the late 19th century but has relied on
resource exploitation
. Guyana became independent of the United Kingdom on 26 May 1966.
Economy and Politics
The slave economy flourished between the abolition of the slave trade in 1807 and emancipation in the 1830s. The wealth largely flowed to a group of absentee slave owners living in Britain, especially in Glasgow and Liverpool.
The economy of British Guiana was completely based on sugar cane production until the 1880s, when falling cane sugar prices stimulated a shift toward rice farming, mining and forestry. However, sugarcane remained a significant part of the economy (in 1959 sugar still accounted for nearly 50%of exports). Under the Dutch, settlement and economic activity was concentrated around sugarcane plantations lying inland from the coast. Under the British, cane planting expanded to richer coastal lands, with greater coastline protection. Until the
abolition of slavery in the British Empire
, sugar planters depended almost exclusively on slave labour to produce sugar. Georgetown was the site of
a significant slave rebellion in 1823
.
In the 1880s gold and diamond deposits were discovered in British Guiana, but they did not produce significant revenue.
Bauxite
deposits proved more promising and would remain an important part of the economy. The colony did not develop any significant manufacturing industry, other than sugar factories, rice mills,
sawmills
, and certain small-scale industries (including a brewery, a soap factory, a biscuit factory and an oxygen-acetylene plant, among others).
The London-based
Booker Group
of companies (Booker Brothers, McConnell & Co., Ltd) dominated the economy of British Guiana. The Bookers had owned sugar plantations in the colony since the early 19thcentury; by the end of the century they owned a majority of them; and by 1950owned all but three. With the increasing success and wealth of the Booker Group, they expanded internationally and diversified by investing in rum, pharmaceuticals, publishing, advertising, retail stores, timber, and petroleum, among other industries. The Booker Group became the largest employer in the colony, leading some to refer to it as "Booker's Guiana".
Indentured workers from India 1850 to 1920 were largely locked in place. Nevertheless a minority achieved mobility. Some secretly fled; others waited until their contracts expired. Indian migration involved three phases: desertion from the plantations; movement settlements and later to urban areas; and intra-regional migration from one Caribbean island to another. The traditional rigid Indian caste system largely collapsed in the colonies.
Guianese served in all British forces during World War II in1939-1945, and enjoyed veterans' benefits afterward. The colony made a small but important financial contribution to the war effort, and it served as a refuge for displaced Jews.
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
Bauxite
Bauxite
is a
sedimentaryrock
with a relatively high
aluminium
content.It is the world's main source of aluminium and
gallium
. Bauxite consists mostly of thealuminium
minerals
gibbsite
(Al(OH)
3
),
boehmite
(γ-AlO(OH)) and
diaspore
(α-AlO(OH)),
mixed
with the two
iron oxides
goethite
(FeO(OH)) and
haematite
(Fe
2
O
3
),the aluminium
clay mineral
kaolinite
(Al
2
Si
2
O
5
(OH)
4
)and small amounts of
anatase
(TiO
2
)and
ilmenite
(FeTiO
3
orFeO.TiO
2
).
[1]
Bauxite appears dull in lusterand is reddish-brown, white, or tan in color.
[2]
In 1821 the
French
geologist
Pierre Berthier
discovered bauxite nearthe village of
Les Baux
in
Provence
, southern
France
.
Processing
Bauxite is usually
strip mined
becauseit is almost always found near the surface of the terrain, with little orno
overburden
.As of 2010, approximately 70% to 80% of the world's dry bauxite production isprocessed first into
alumina
and then into aluminium by
electrolysis
.
[8]
Bauxiterocks are typically classified according to their intended commercialapplication: metallurgical, abrasive, cement, chemical, and refractory.
Usually, bauxite ore is heated in a pressure vessel along witha
sodium hydroxide
solution at a temperatureof 150 to 200 °C (300 to 390 °F). At these temperatures, the
aluminium
isdissolved as
sodium aluminate
(the
Bayer process
).The aluminium compounds in the bauxite may be present as
gibbsite
(Al(OH)
3
),
boehmite
(AlOOH)or
diaspore
(AlOOH);the different forms of the aluminium component will dictate the extractionconditions. The undissolved waste,
bauxite tailings
,after the aluminium compounds are extracted contains
iron oxides
,
silica
,
calcia
,
titania
andsome un-reacted
alumina
. After separation of the residue by filtering, puregibbsite is precipitated when the liquid is cooled, and then seeded withfine-grained aluminium hydroxide. The gibbsite is usually converted into
aluminium oxide
,Al
2
O
3
, by heating in rotary kilns or fluid flashcalciners to a temperature in excess of 1,000 °C (1,830 °F). Thisaluminium oxide is dissolved at a temperature of about 960 °C(1,760 °F) in molten
cryolite
.Next, this molten substance can yield metallic aluminium by passing an
electric current
throughit in the process of electrolysis, which is called the
Hall–Héroult process
, named after its Americanand French discoverers.
Prior to the invention of this process, and prior to the
Deville process
, aluminium ore was refinedby heating ore along with elemental
sodium
or
potassium
ina
vacuum
.The method was complicated and consumed materials that were themselvesexpensive at that time. This made early elemental aluminium more expensivethan
gold
.
[9]
Source of gallium
Bauxite is the main source of the rare metal
gallium
.
[10]
During the processing of bauxite to
alumina
inthe
Bayer process
, gallium accumulates in the
sodium hydroxide
liquor.From this it can be extracted by a variety of methods. The most recent is theuse of
ion-exchange resin
.
[11]
Achievableextraction efficiencies critically depend on the original concentration in thefeed bauxite. At a typical feed concentration of 50 ppm, about 15 percent ofthe contained gallium is extractable.
[11]
Theremainder reports to the
red mud
and
aluminium hydroxide
streams.
[12]
Old Collection
British Guiana
Guyana
Postage Stamps Blocks
International Shipping will cost more.
Item sold for more than needs to have tracking.
2021 USPS Postage Rates and Prices
REGISTERED MAIL FEE is .30
INTERNATIONAL POSTAGE is .24 (2 oz)
INTERNATIONAL POSTAGE is .28 (3 oz)
TOTAL POSTAGE and FEES equal .58
Please check cost with seller before buying.
Thank you!
Combined Shipping for Multiple Purchases.
Shipped with United States Postal Service (USPS) First Class Mail.